- Department of Chemistry, IIT Hyderabad
- +91 (40) 2301 6015
- office@chy.iith.ac.in

In circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, the absorbance of right and left circularly polarized light by molecules in solution is measured.
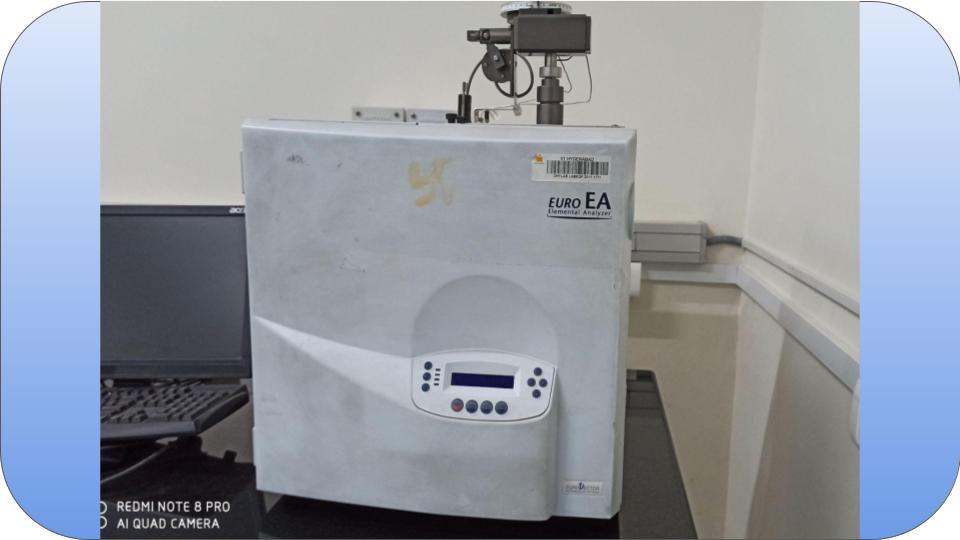

The CHNS(O) Analyzer find utility in determining the percentages of Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulphur and Oxygen of organic compounds, based on the principle of "Dumas method" which involves the complete and instantaneous oxidation of the sample by "flash combustion".

TGA measures weight change of a sample over a temperature range, DSC measures heat flow of a sample over a temperature range, and DTA measures heat differences between a reference sample and a sample of interest over a temperature range.

With an ESR instrument, a static magnetic field and microwaves are used to observe the behavior of the unpaired electrons in the material being studied. The study of the behavior of the electrons in a sample gives information about the condition of the sample.
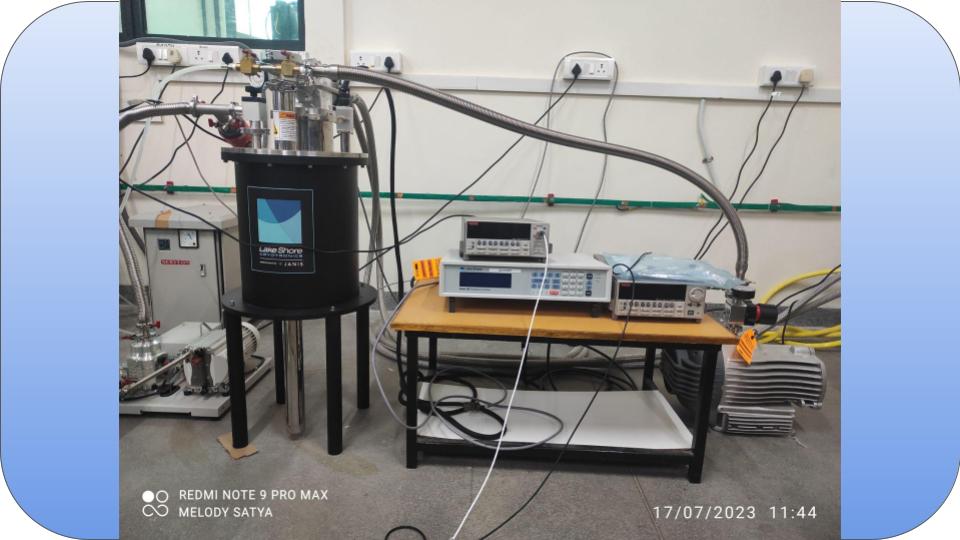

A cryostat is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium.
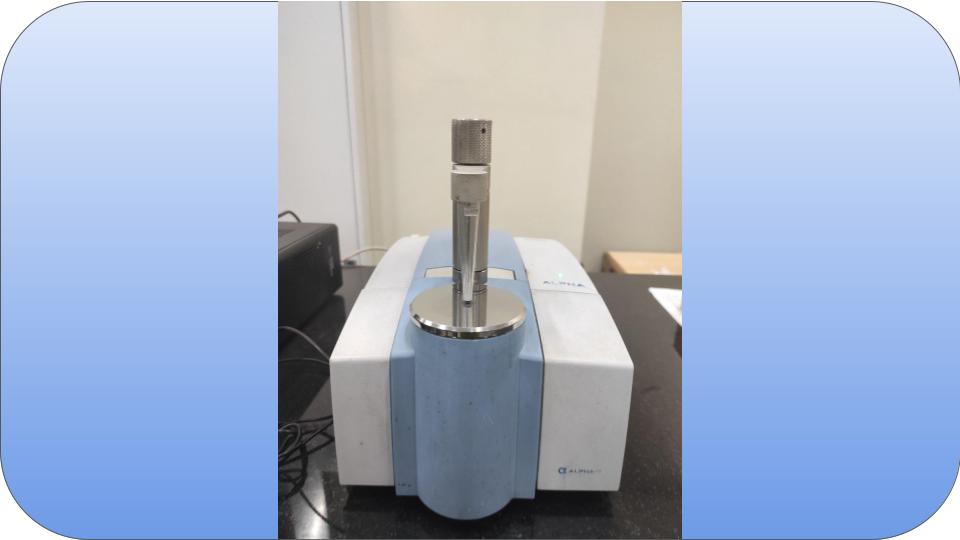

FTIR spectroscopy is a technique that uses mid-infrared energy to analyze the molecular structure and composition of substances by measuring the absorption of specific frequencies of infrared light, providing a unique fingerprint for identification and analysis.
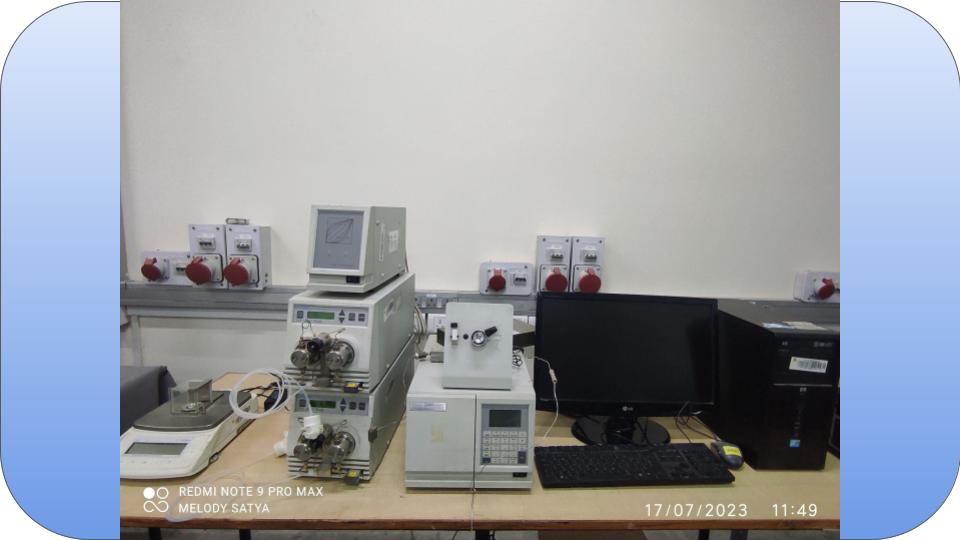

HPLC is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.
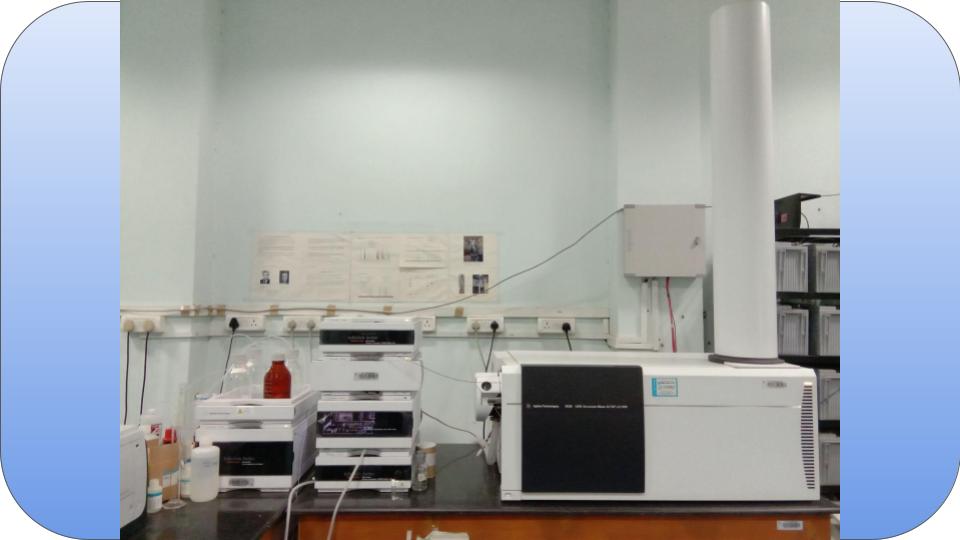

High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) uses mass spectrometers capable of high resolution, as well as high mass accuracy measurements. These instruments can be used to distinguish between compounds with the same nominal mass, determine elemental compositions, and identify unknowns.
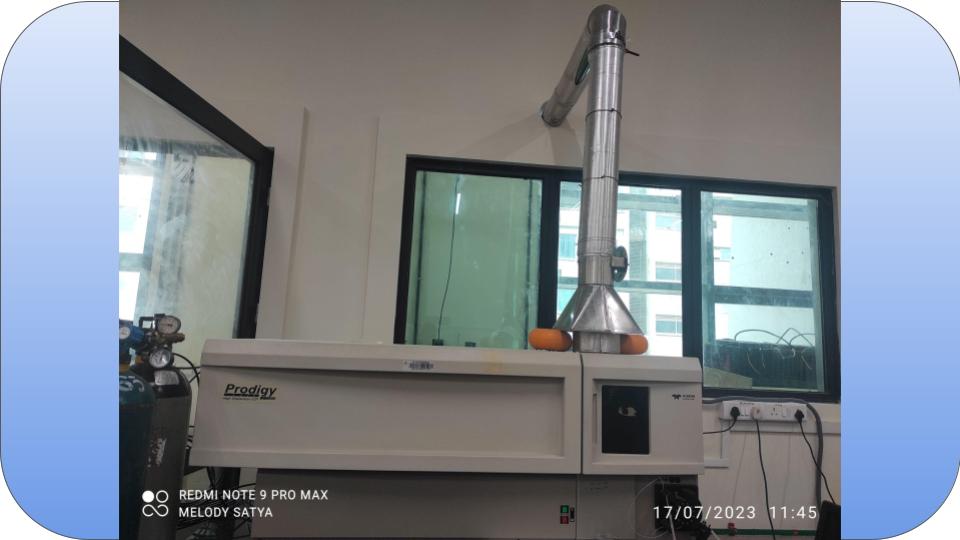

ICP-OES is an analytical technique used to determine how much of certain elements are in a sample. The ICP-OES principle uses the fact that atoms and ions can absorb energy to move electrons from the ground state to an excited state.
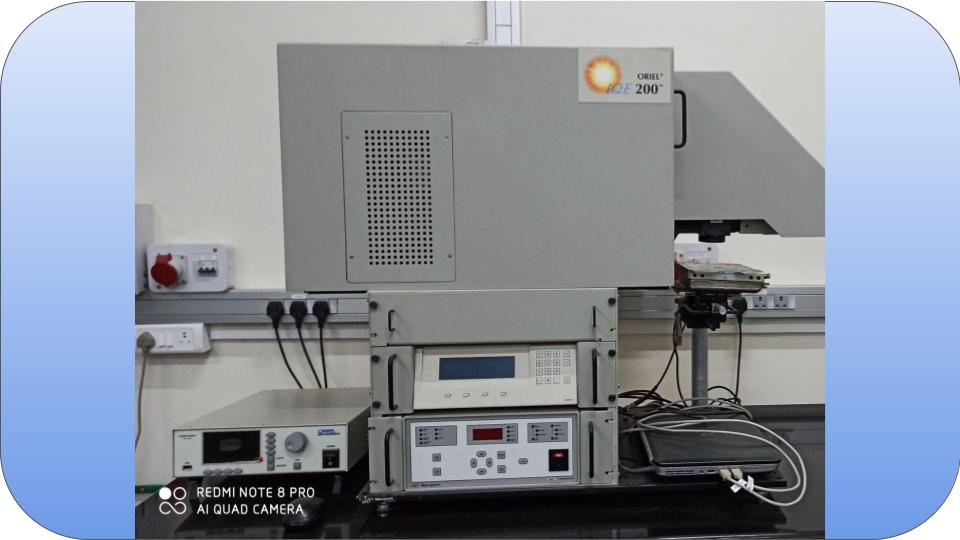

to be updated.
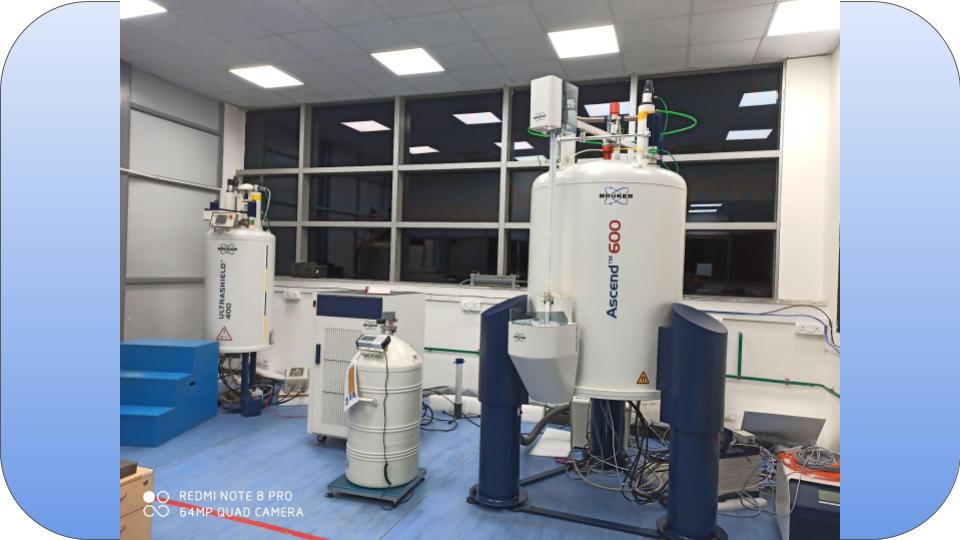

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy is a research tool for organic chemists which can determine both the physical and chemical properties of atoms or molecules. The NMR Spectroscopy relies on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance and provides detailed information about the structure, reaction state, and chemical environment of molecules.
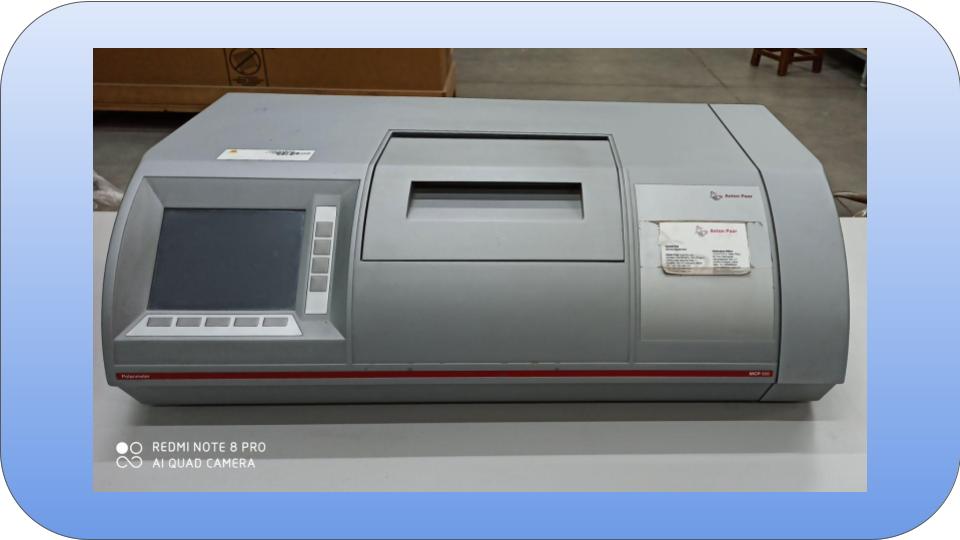

A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance.
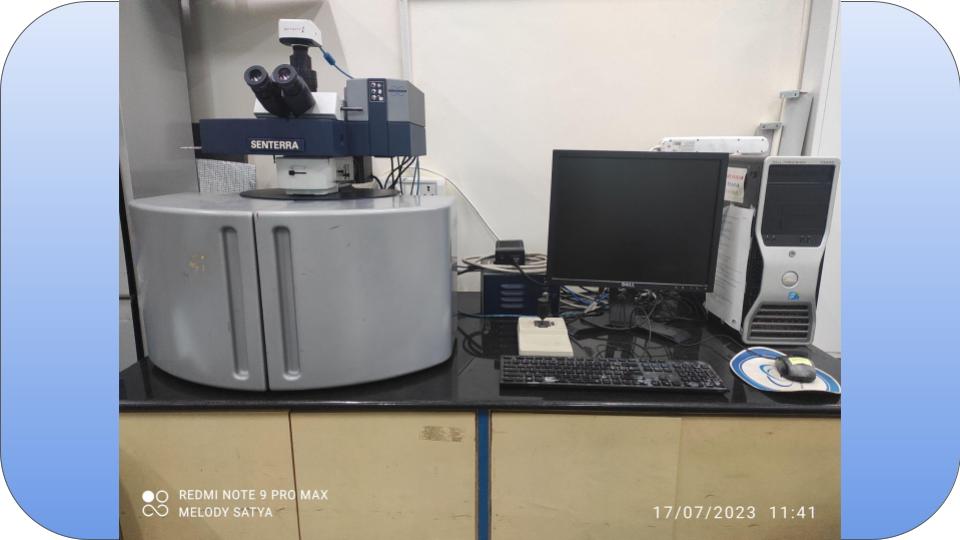

Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique which provides detailed information about chemical structure, phase and polymorphy, crystallinity and molecular interactions.
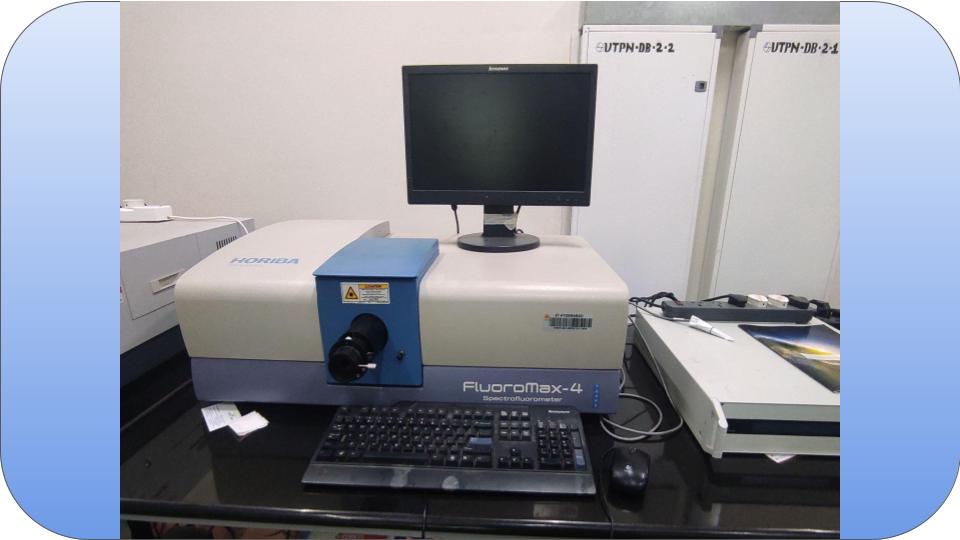

A spectrofluorometer is an instrument which takes advantage of fluorescent properties of some compounds in order to provide information regarding their concentration and chemical environment in a sample.

The main purposes for using UPLC are for identifying and quan- tifying the individual components of the complicated samples (e.g. botanical, dietary supplements, biological samples and et al).
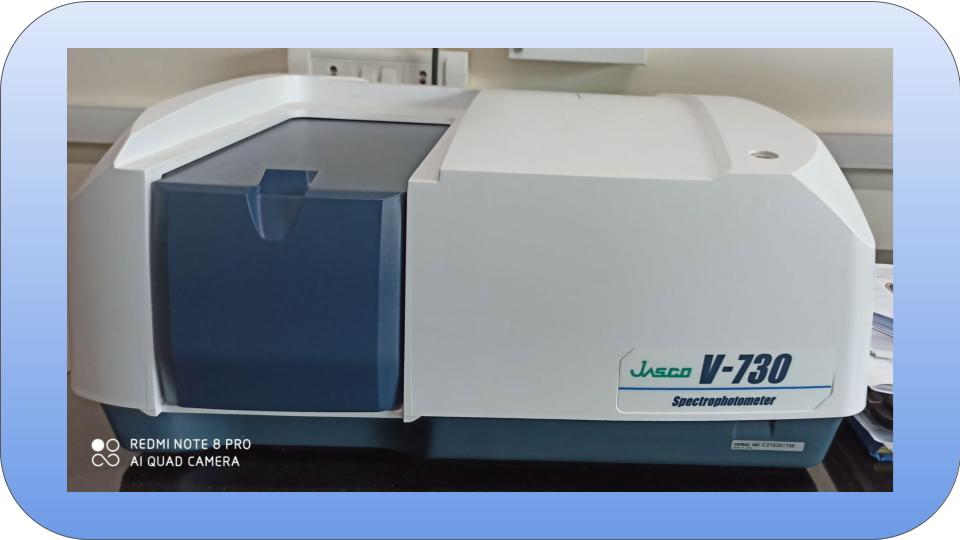

A spectrophotometer is an instrument that measures the amount of photons (the intensity of light) absorbed after it passes through sample solution. With the spectrophotometer, the amount of a known chemical substance (concentrations) can also be determined by measuring the intensity of light detected.
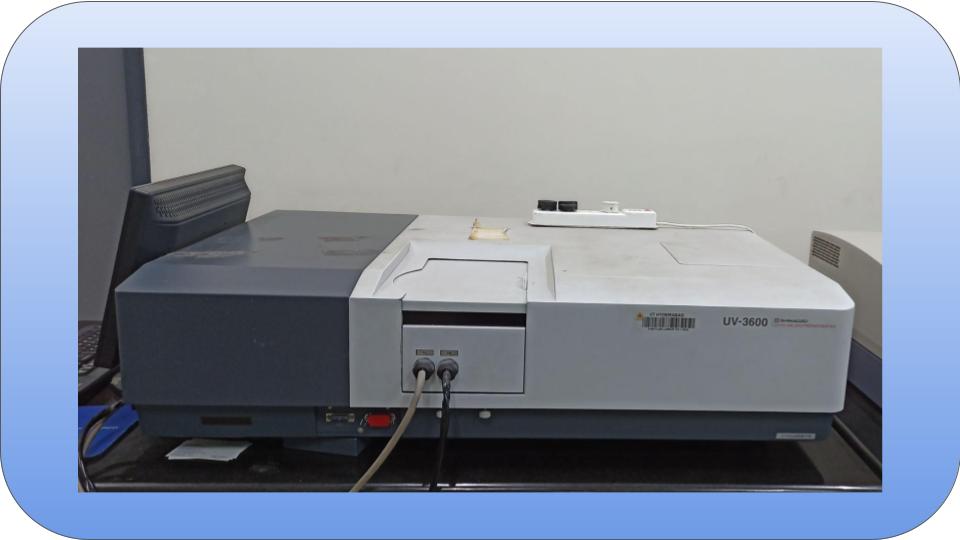

UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer UV-3600 using an integrating sphere attachment enables the measurement of optical characteristics of solid samples, thin films and foils.
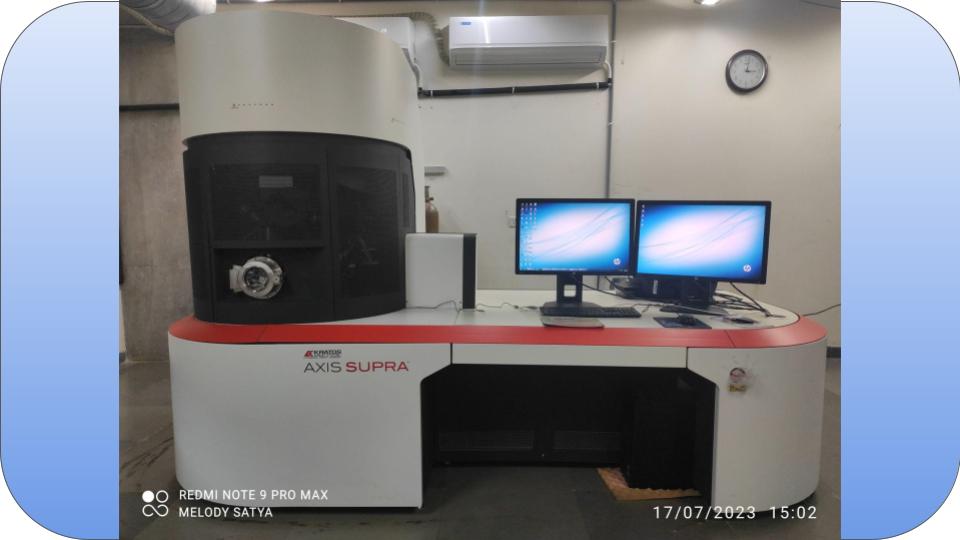

XPS is a technique for analyzing a material's surface chemistry. XPS can measure elemental composition as well as the chemical and electronic state of the atoms within a material.
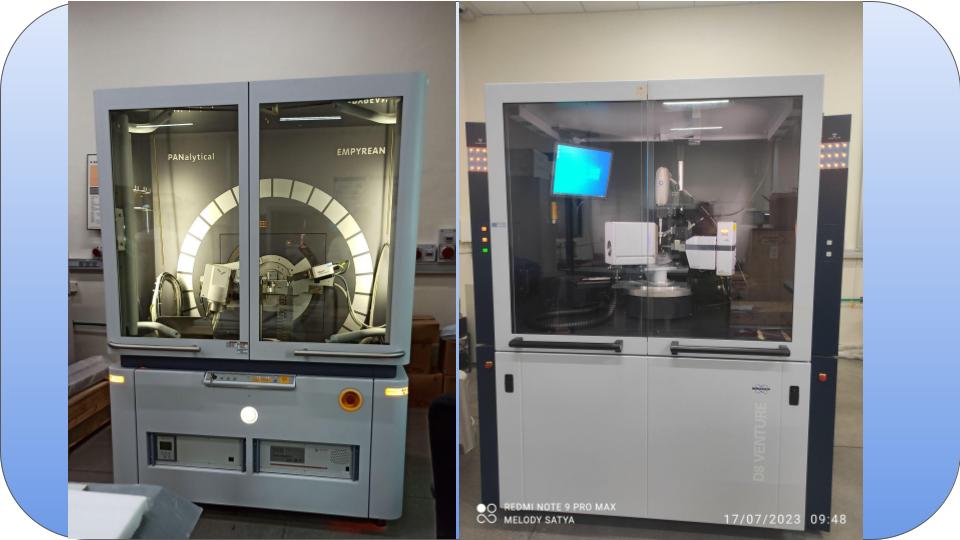

X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a nondestructive technique that provides detailed information about the crystallographic structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials.
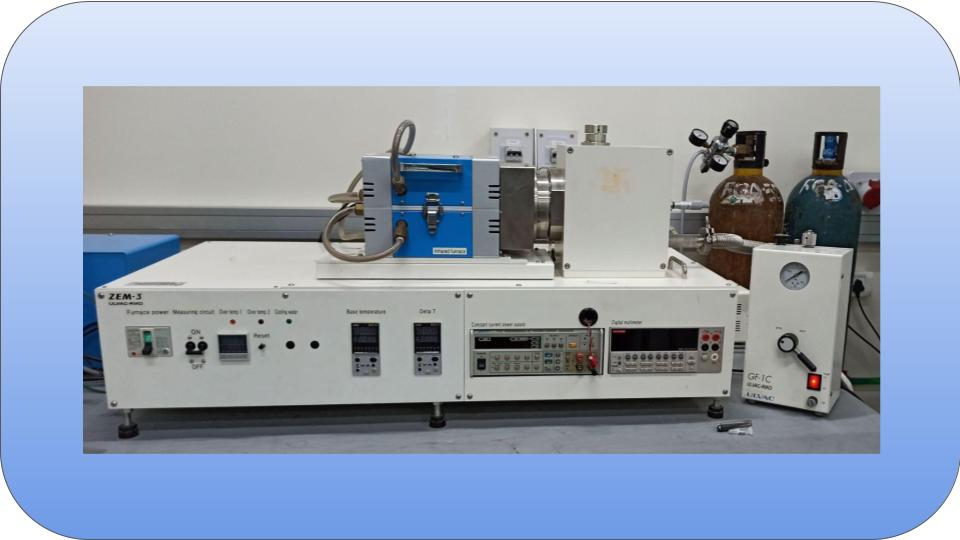

Evaluate the thermoelectric properties of a wide variety of materials including semiconductors, ceramics, and metals.
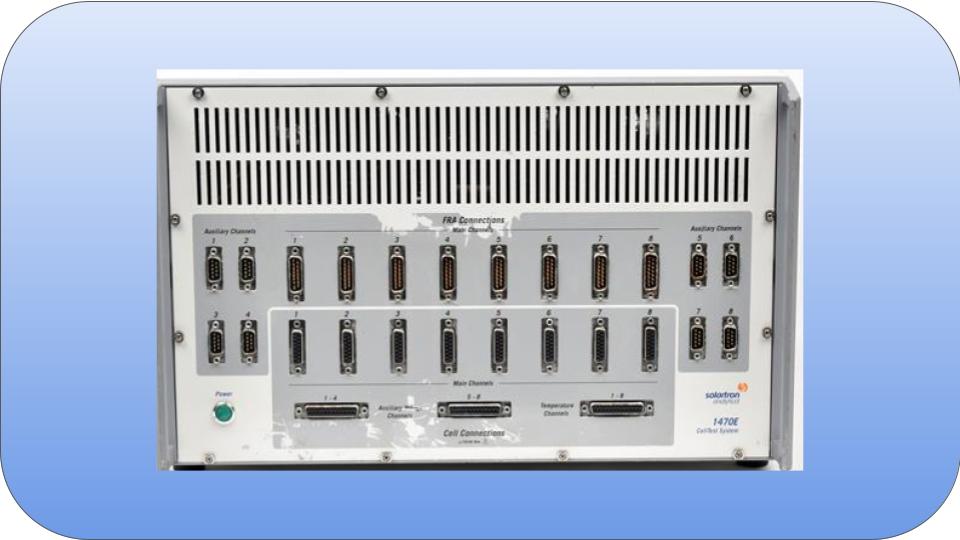

Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is a powerful technique used for the analysis of interfacial properties related to bio-recognition events occurring at the electrode surface, such as antibody–antigen recognition, substrate–enzyme interaction, or whole cell capturing.
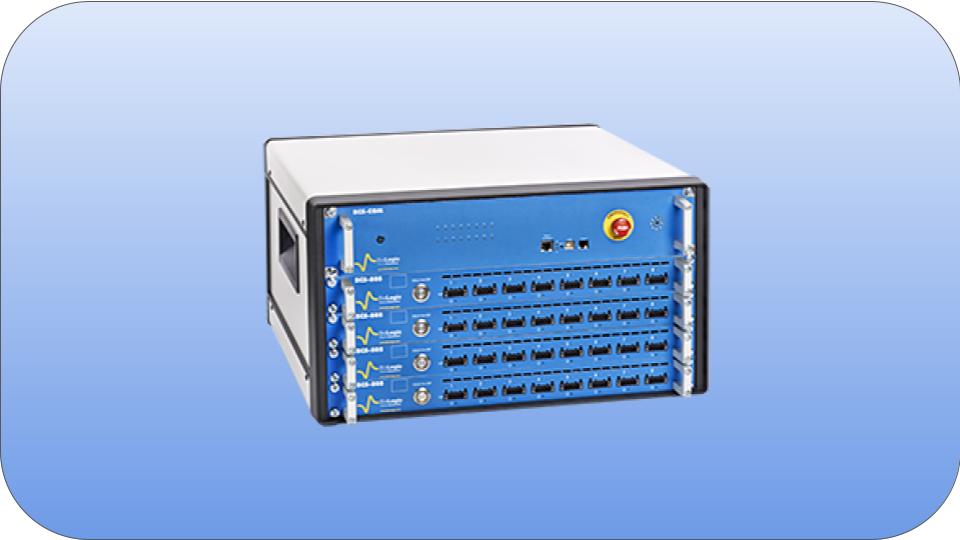

A battery cycler will analyse battery function through charge/discharge cycles, by measuring the cells response over time. During battery cycling, a number of parameters can be measured, including capacity, efficiency of the battery and self-discharge.
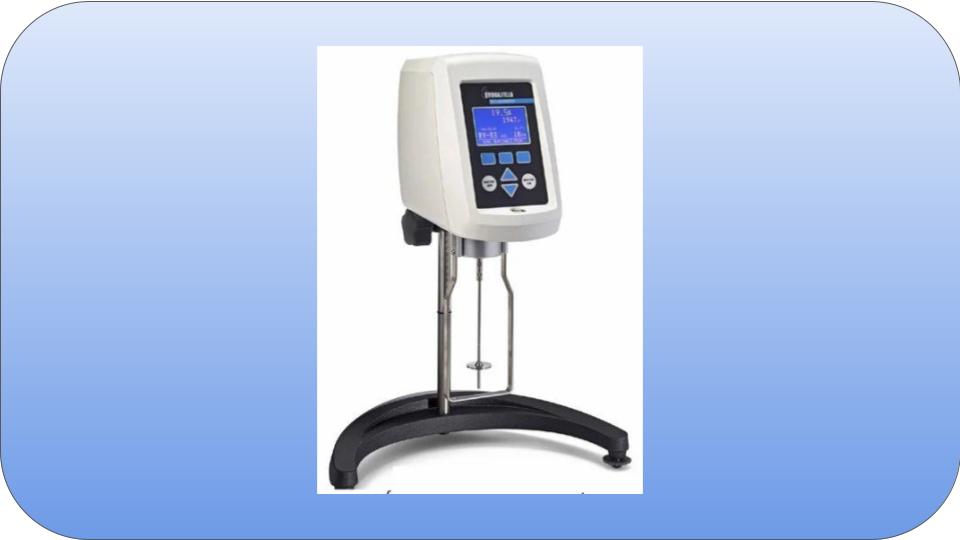
Viscometers are instruments that measure the fluid flow and viscosity of liquids.